导言
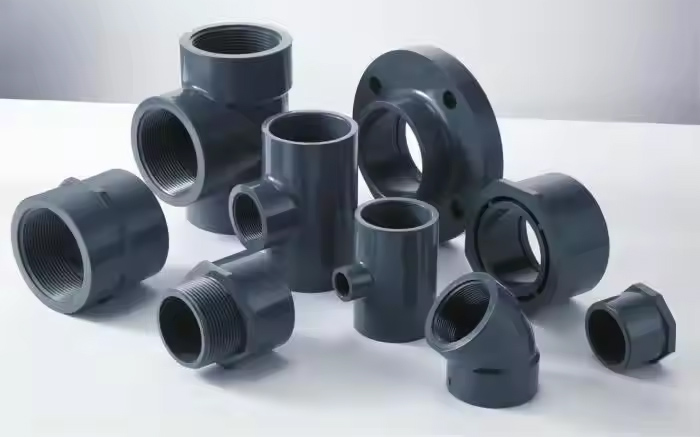
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipe is one of the most widely used plastic piping materials for water supply, drainage, irrigation, and industrial applications. It’s valued for its corrosion resistance, light weight, smooth interior surface, and long service life.
Types of PVC Pipe
The first thing to know is that not all PVC is the same. The two main types you’ll encounter are PVC Schedule 40 和 PVC DWV.
1. PVC Schedule 40 (Pressure Pipe)
- Instructions:This is the most common and versatile type of PVC pipe.
- Purpose:Designed to handle pressurized water and other fluids.
- Common Uses:Residential water supply lines, irrigation systems, pool and spa plumbing, underground utilities, and many DIY projects (like furniture or greenhouses).
- Color:Usually white, but can also be dark gray (for electrical conduit) or other colors.
- Key Feature:Has thicker walls than DWV pipe, allowing it to withstand internal pressure.
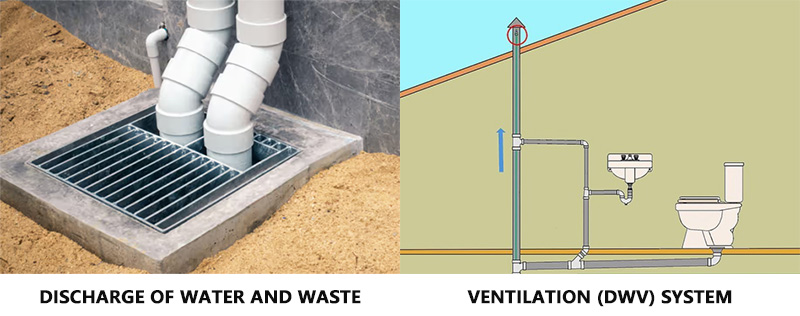
2. PVC DWV (Drain, Waste, Vent)
- Instructions:As the name implies, this type is specifically for non-pressure applications.
- Purpose:Designed to carry wastewater and sewage away from sinks, toilets, and showers, and to provide venting for the plumbing system.
- Common Uses:All the drain lines inside your home’s walls and under the floors.
- Color:Almost always a creamy, off-white color.
- Key Feature:Has thinner walls than Schedule 40 because it doesn’t need to handle pressure. Its fittings have a wider, smoother interior to prevent clogs and allow waste to flow easily. Never use DWV pipe for pressurized applications.
3. Other Common Vinyl Pipes (Often Confused with PVC)
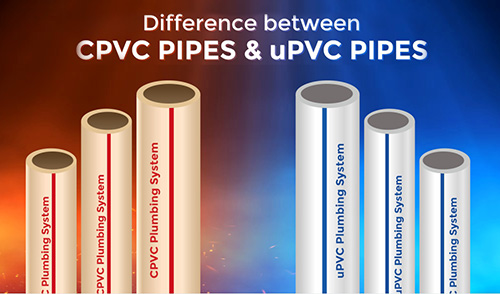
(1)CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride):
- Identified by:Its distinctive cream or light yellow color.
- Key Feature:Can handle higher temperatures than PVC, making it suitable for hot and cold water supply lines inside your home.
- Note:It requires special CPVC cement and is not interchangeable with standard PVC fittings.
(2)ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene):
- Identified by:Its black color.
- Common Use:Primarily used for drain, waste, and vent (DWV) systems, similar to PVC DWV. It’s common in some regions and for underground outdoor use.
- Note:Requires special ABS cement and is not glued to PVC without a special transition cement.

Understanding PVC Pipe Sizes
This is the most confusing part for beginners. PVC pipe sizes are “nominal,” meaning they are a name for the size, not a direct measurement.
1. The Two Key Measurements:
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): This is the approximate inner diameter based on historical standards. A “1/2-inch” pipe does not have a 1/2-inch inner diameter.
Outside Diameter (OD): This is a fixed, consistent measurement. All 1/2-inch Schedule 40 pipes have the exact same outside diameter, regardless of the manufacturer. This ensures that fittings are universal.
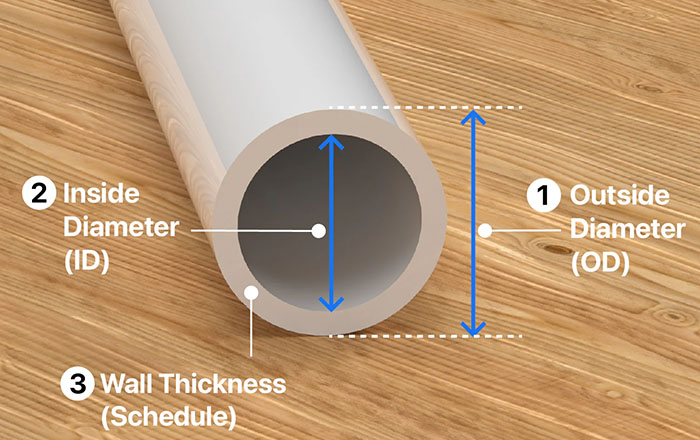
Why is this important? When you glue a fitting onto a pipe, you are connecting based on the Outside Diameter.
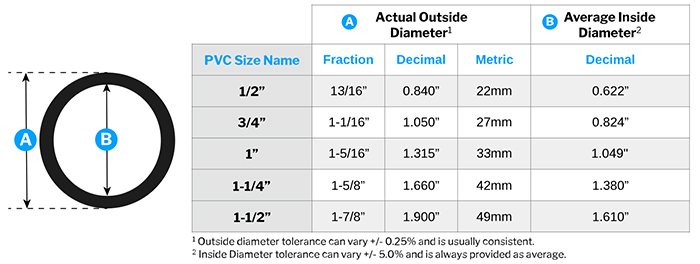
2. Common PVC Pipe Sizes:
| Nominal Size | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|
| 1/2″ | Sink faucet supply lines, low-flow irrigation |
| 3/4″ | Main water supply line to a house, common for irrigation |
| 1″ | Main water supply, larger irrigation lines |
| 1-1/4″ | Drain lines for sinks and bathtubs |
| 1-1/2″ | Drain lines for kitchen sinks, washing machines, shower stalls |
| 2″ | Drain lines for laundry sinks, some toilet branches |
| 3″ | Main toilet drain lines |
| 4″ | Main house sewer lines, underground drainage |
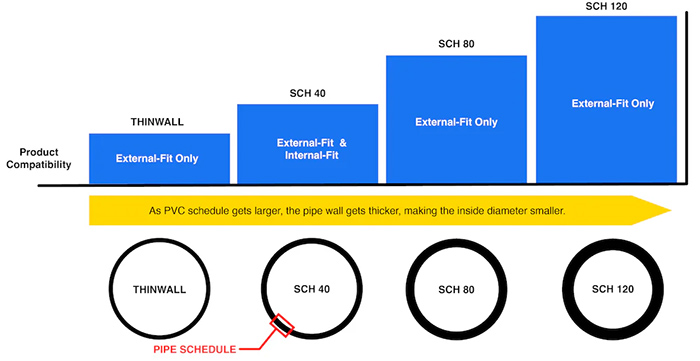
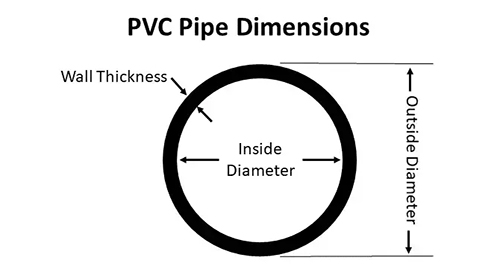
Wall Thickness Grades (Schedules)
The “Schedule” (often abbreviated as “SCH”) refers to the wall thickness of the pipe. A higher schedule number means a thicker, stronger wall.
1. Common Schedules:
| 时间安排 | Description & Common Uses |
|---|---|
| 附表 40 | "(《世界人权宣言》) most common grade. Strong enough for most pressure and structural applications. Used for water supply, irrigation, and DIY projects. |
| 附表 80 | Has a thicker wall than Schedule 40, making it stronger and more durable. Used for higher-pressure industrial applications or where extra physical strength is needed. It has the same Outside Diameter as Schedule 40, but a smaller Inside Diameter. |
| Schedule 120 | An even thicker wall, used for very high-pressure applications. Less common for general use. |
| SDR (Dimension Ratio) | Common for underground water mains and sewer lines. The DR number (e.g., DR 18, DR 35) is a ratio of the pipe’s outside diameter to its wall thickness. A lower DR number means a thicker wall. |
2. SDR vs. Schedule:
- Schedule is a legacy term that defines a set of wall thicknesses.
- SDR (Standard Dimension Ratio) is a more modern, calculated system where the wall thickness is directly proportional to the diameter. SDR 35 is a very common grade for underground non-pressure sewer and drain pipe.

3. Quick Comparison Table: Schedule 40 vs. Schedule 80
| 特点 | 附表 40 | 附表 80 |
|---|---|---|
| 壁厚 | 标准 | Thicker |
| 压力等级 | Lower | Higher (about 2/3 stronger) |
| Inside Diameter | Larger | Smaller (for the same nominal size) |
| 费用 | Less Expensive | More Expensive |
| 重量 | Lighter | Heavier |
| 颜色 | Usually White | Usually Dark Gray |

How to Choose the Right PVC Pipe:
1. What is the application?
- Pressurized Water? -> PVC Schedule 40 或 CPVC Sch40.

- Drain Line (Sink, Toilet)? -> PVC DWV.

- Underground Drainage? -> PVC SDR 35.

- High-Pressure Industrial? -> PVC Schedule 80.

- DIY Structure (e.g., Greenhouse)? -> PVC Schedule 40.

2. What size do you need?
- Measure the existing pipe or check the specifications of what you’re connecting to. Remember, you match based on the Nominal Size.
- Always check your local plumbing codes for any restrictions or required materials, especially for projects inside your home.
摘要
PVC pipes are available in multiple types (压力, 排水, conduit), sizes, and wall thickness grades (Schedule or PN) to suit various applications. Understanding these distinctions helps ensure optimal performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness in your piping system.
关于卓信塑业
SAM-UK 是专业人士 19 岁以上 生产乙烯基建筑型材产品的制造商,以及 聚氯乙烯 , CPVC , PPH , PPR , 聚丙烯 管材和管件、阀门、水龙头等。我们拥有 SGS\SONCAP\ISO9001\CE\NSF支持颜色/尺寸定制。欢迎咨询 目录 和 产品您可以通过电子邮件与我们联系 [email protected]